 Updated:2024-11-25
Updated:2024-11-25 1、Product Overview and Usage
Ⅰ、Electrolytic copper foil is used in lithium-ion batteries as a carrier for negative electrode active materials and as a collector and transporter for negative electrode electron flow.
Ⅱ、Before 2000, the only use of electrolytic copper foil was for manufacturing printed circuit boards, and rolled copper foil was used for the negative electrode of lithium batteries.
Ⅲ、With the gradual improvement of process technology and production equipment accuracy, high-performance electrolytic copper foil began to replace rolled copper foil after 2000, making electrolytic copper foil widely used in the lithium battery industry.

Coiled copper foil
Roll shaped copper foil: Roll shaped copper foil is an important electrolytic material with high conductivity, high thermal conductivity, good plasticity, and corrosion resistance, and is widely used in multiple fields.
• The rolled copper foil is the continuous metal layer at the bottom of the circuit board, usually adhered to the insulation layer, and formed into circuit patterns through printing and etching processes.
• In the fields of electronics and communication, rolled copper foil can be used for electromagnetic shielding and anti-static applications, providing good conductivity and electromagnetic shielding effect.
• The transportation and storage of rolled copper foil require specialized packaging boxes, such as copper foil packaging boxes with fixed structures, to prevent damage to the copper foil due to shaking during transportation.
• There are numerous suppliers of rolled copper foil, offering products in different materials, widths, and thicknesses to meet the needs of various fields.
• Manufacturers of rolled copper foil are also constantly improving their research and development capabilities, tackling core technology research and development, in order to produce higher quality and thinner products. Gansu Hailiang New Energy Materials Co., Ltd. is one of the outstanding companies among them.
Roll shaped copper foil plays an important role in modern industry due to its unique properties and wide range of applications.

Negative electrode slurry coating
Negative electrode slurry coating: Negative electrode slurry coating is a key step in the manufacturing process of lithium batteries, directly affecting battery performance and lifespan.
• Negative electrode slurry composition: generally composed of active material, conductive agent, binder, and solvent. The active material is a carrier for storing plasmons, the conductive agent improves conductivity, the binder fixes the material, and the solvent forms a slurry;
• Coating technology: There are mainly uniform coating method, scraping coating method, rolling coating method, etc., and the choice depends on the battery requirements and production process. During the coating process, equipment such as scraper rollers can remove foreign objects from the substrate to ensure coating quality.
• The purpose of coating process is to evenly apply the positive and negative electrode slurry on the substrate to form a film layer with special functions. Pre coating coating and slurry coating are the main methods.
• Preparation of negative electrode slurry: including preparing carboxymethyl cellulose sodium aqueous solution, mixing with conductive agent, adding graphite, etc., to finally obtain negative electrode slurry.
Optimizing the composition and coating technology of negative electrode slurry can improve the capacity, cycle life, and safety performance of batteries, making them more stable and reliable.

Lithium battery negative electrode
Lithium battery negative electrode: It is the lower potential end of the battery, mainly made by mixing negative electrode active material, binder, and additives, and evenly coated on both sides of the copper foil.
• Material types: Currently, commercially available lithium-ion batteries mainly use graphite as the negative electrode material. In addition, there are tin based negative electrode materials, lithium containing transition metal nitride negative electrode materials, alloy based negative electrode materials, and nanoscale negative electrode materials.
• Performance characteristics: The graphite negative electrode has a multi-layer structure that can accommodate lithium atoms and achieve the charging and discharging process of lithium ions. The theoretical specific capacity of silicon-based negative electrode materials is about 10 times that of graphite negative electrodes, but there is an expansion effect.
• Development trend: In order to improve the energy density of lithium batteries, it is necessary to develop negative electrode materials with higher specific capacity, such as silicon carbon negative electrodes. Meanwhile, companies have developed corresponding functional adhesive materials (PAA) to suppress and solve the expansion effect of silicon-based negative electrodes.
The negative electrode of a lithium battery is an important component of the battery, and its material type and performance characteristics have a significant impact on the overall performance of the battery.
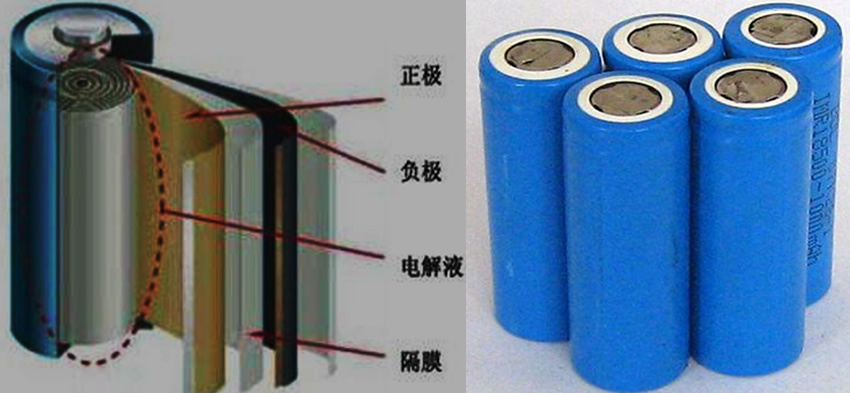
Cylindrical lithium battery structure
The structure of a cylindrical lithium battery mainly includes the following parts: shell, cap, positive electrode, negative electrode, separator, electrolyte, PTC element, gasket, and safety valve.
Structural composition:
Shell: Usually a nickel plated steel shell, used as the negative electrode of the battery.
Cap: serves as the positive electrode of the battery.
Positive electrode: Lithium cobalt alloy material is usually used.
Negative electrode: using carbon material.
Diaphragm: Used to isolate positive and negative electrodes to prevent short circuits.
Electrolyte: A medium that provides ion transport.
PTC component: used for over temperature protection.
Gasket: Used for sealing batteries.
Safety valve: prevents excessive pressure inside the battery. Positive electrode: Lithium cobalt alloy material is usually used.
Common models and specifications:
10440 battery: diameter 10mm, height 44mm, small capacity, suitable for mini electronic products.
14500 battery: diameter 14mm, height 50mm, moderate capacity, suitable for consumer electronics devices.
16340 battery: diameter 16mm, height 34mm, suitable for strong light flashlights, etc.
18650 battery: diameter 18mm, height 65mm, high energy density, widely used in small appliances such as mobile phones, laptops, etc.
21700 battery: diameter 21mm, height 70mm, higher energy density, suitable for electric vehicles, solar energy, etc.
26650 battery: diameter 26mm, height 65mm, large capacity, suitable for power batteries.
32650 battery: diameter 32mm, height 65mm, strong continuous discharge capability.
Manufacturing process and material selection
The manufacturing process of cylindrical lithium batteries involves rolling different battery layers into a cylindrical drum and then placing it into a metal can. The shell is usually made of nickel plated steel plate to provide good conductivity and mechanical strength.
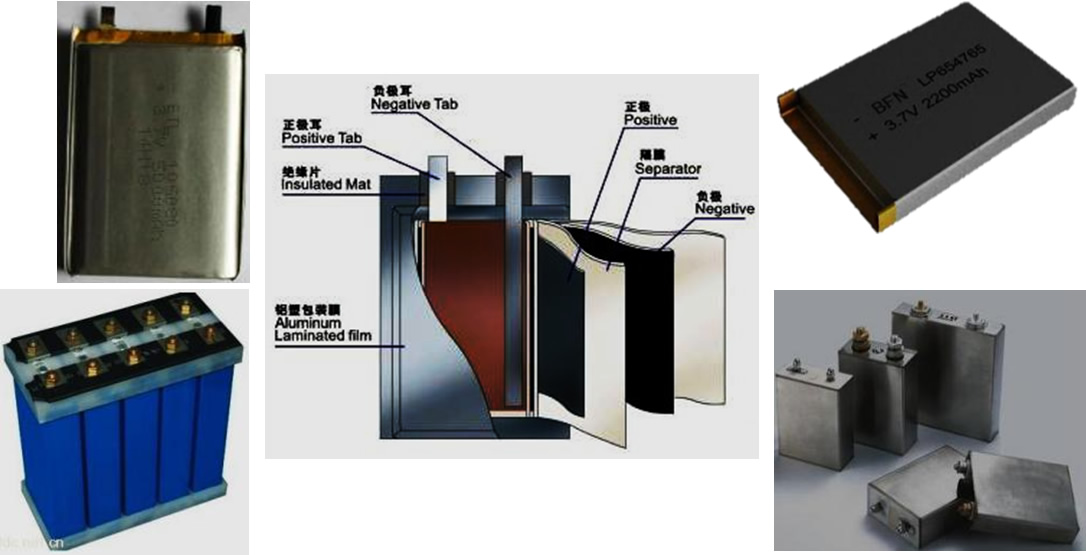
Square lithium battery structure
Square lithium batteries are mainly composed of a top cover, a shell, a positive electrode plate, a negative electrode plate, a separator, insulation components, and safety components.
Top cover and shell: laser welded to form a sealed whole, the top cover also includes positive and negative poles, explosion-proof devices, etc., with functions such as fixing, sealing, current conduction, pressure relief, and fuse protection.
Positive and negative plates: The positive active material is usually lithium manganese oxide, lithium cobalt oxide, or nickel cobalt lithium manganese oxide, while the negative active material is graphite or carbon with a graphite like structure. The conductive electrode fluid uses electrolytic aluminum foil and electrolytic copper foil respectively.
Diaphragm: It is a specially formed polymer film with a microporous structure that allows lithium ions to pass freely, but electrons cannot pass through.
Safety components: including needle safety device (NSD) and overcharge protection device (OSD), used to prevent safety risks during battery thermal runaway and overcharging.
In addition, square lithium batteries also include organic electrolytes and the characteristic of customized production according to product size.
2、CLASSIFICATION
• Product category
Double sided smooth (code: LBEC-01)
Single sided smooth (code: LBEC-02)
Double sided rough (code: LBEC-03)
Double sided roughened (code: LBEC-04)
Note: LB—lithium battery; EC—electrolytic copper foil; Number—Product code
• thickness
6μm、7μm、8μm、9μm、10μm、12μm、15μm
• product description:
Double sided smooth (code: LBEC-01): characterized by a double-sided smooth surface. This copper foil is suitable for the production of lithium-ion batteries, polymer lithium-ion batteries, and power lithium-ion batteries, and its surface quality, composition, and performance all comply with relevant standards and regulations. The dual sided design helps to improve the processability and service life of copper foil, while meeting the high requirements for material performance in battery manufacturing. During the production process, manufacturers will strictly control the various indicators of copper foil to ensure its stable and reliable quality.
Single sided smooth (code: LBEC-02): ordinary single-sided treatment, with ultra-thin characteristics, good ductility, and good coating properties when adhered.
Double sided rough (code: LBEC-03): Advanced double-sided treatment of lithium-ion battery copper foil, with ultra-thin characteristics that can be coated with double-sided paste, and has the advantage of high load-bearing capacity. It has good coating properties when adhered.
Double sided roughened (code: LBEC-04): After double-sided roughening treatment, it has specific performance requirements, such as surface roughness, copper content, tensile strength, elongation, etc.
3、production process
1.Copper dissolution
Copper dissolution process for liquid production
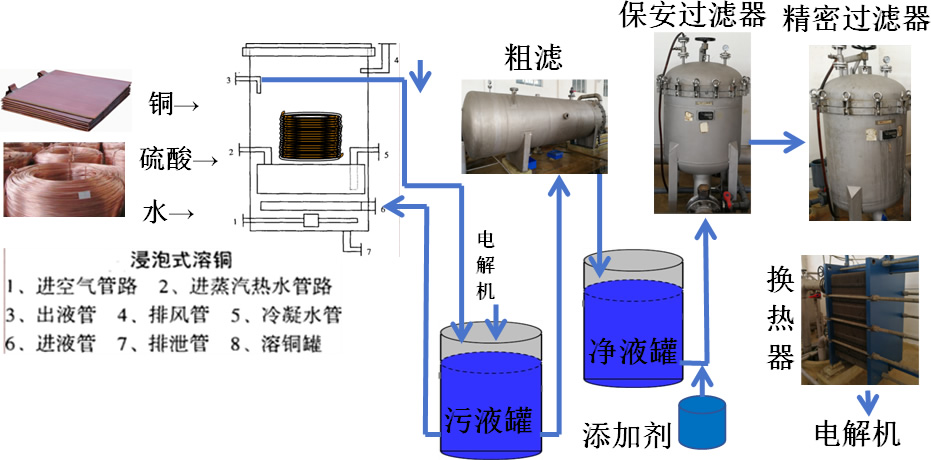
The copper dissolution process is one of the key steps in the production of electrolytic copper foil, mainly including three main stages: raw material preparation, copper dissolution reaction, and filtration.
1) Raw material preparation: The main raw material is copper wire, with a copper content of over 95%. The larger the surface area of the copper wire, the better, and there should be small gaps between the copper materials to increase the reaction area.
2) Copper dissolution reaction: Put the processed copper wire into a copper dissolution tank containing sulfuric acid, and add oxygen (usually through compressed air blowing) for oxidation reaction to promote the dissolution of copper. The reaction speed is related to the total surface area and air volume of the copper material in the tank.
3) Filtration: After the dissolution of copper, the copper sulfate liquid is filtered to remove impurities and undissolved substances, ensuring the purity of the electrolyte.
• Principle of Copper Melting Liquid Production:
Place copper wire, copper plate and other raw materials in a copper dissolution tank. Under certain temperature conditions, oxygen in the air reacts to produce copper oxide, which then comes into contact with a solution containing sulfuric acid. Copper oxide reacts with sulfuric acid to produce a copper sulfate solution.
reaction equation:
2Cu+O2=2CuO
CuO+H2SO4=CuSO4+H2O
2.Electrolytic foil+anti oxidation treatment
• Electrolytic foil:
The process of producing foil through electrolysis in a specialized electrolytic machine. The electrolytic machine consists of main components such as a titanium cathode roller, a semi-circular electrolytic cell, and a DSA anode. Under the action of direct current, divalent copper ions in the copper sulfate electrolyte inside the electrolytic machine move towards the interface of the cathode roller, resulting in 2e, which is reduced to copper atoms and deposited on the smooth surface of the rotating cathode roller. By adding appropriate additives to control the microstructure of the copper foil surface, a rolled copper foil is formed under continuous peeling and winding conditions.
• Reaction equation for electrolytic copper foil
Cathodic main reaction:Cu2++2e→Cu↓
Cathodic side reaction:Cu2++e→Cu+
anode:2OH--2e→2H++O2↑
The entire process is not only a copper deposition reaction, but also an acid making process because oxygen runs away and H+、SO42- combine to form H2SO4.
The copper dissolution process is one of the key steps in the production of electrolytic copper foil, mainly including three main stages: raw material preparation, copper dissolution reaction, and filtration.
1) Raw material preparation: The main raw material is copper wire, with a copper content of over 95%. The larger the surface area of the copper wire, the better, and there should be small gaps between the copper materials to increase the reaction area.
2) Copper dissolution reaction: Put the processed copper wire into a copper dissolution tank containing sulfuric acid, and add oxygen (usually through compressed air blowing) for oxidation reaction to promote the dissolution of copper. The reaction speed is related to the total surface area and air volume of the copper material in the tank.
3) Filtration: After the dissolution of copper, the copper sulfate liquid is filtered to remove impurities and undissolved substances, ensuring the purity of the electrolyte.
• Principle of Copper Melting Liquid Production:
Place copper wire, copper plate and other raw materials in a copper dissolution tank. Under certain temperature conditions, oxygen in the air reacts to produce copper oxide, which then comes into contact with a solution containing sulfuric acid. Copper oxide reacts with sulfuric acid to produce a copper sulfate solution.
reaction equation:
2Cu+O2=2CuO
CuO+H2SO4=CuSO4+H2O
2.Electrolytic foil+anti oxidation treatment
• Electrolytic foil:
The process of producing foil through electrolysis in a specialized electrolytic machine. The electrolytic machine consists of main components such as a titanium cathode roller, a semi-circular electrolytic cell, and a DSA anode. Under the action of direct current, divalent copper ions in the copper sulfate electrolyte inside the electrolytic machine move towards the interface of the cathode roller, resulting in 2e, which is reduced to copper atoms and deposited on the smooth surface of the rotating cathode roller. By adding appropriate additives to control the microstructure of the copper foil surface, a rolled copper foil is formed under continuous peeling and winding conditions.
• Reaction equation for electrolytic copper foil
Cathodic main reaction:Cu2++2e→Cu↓
Cathodic side reaction:Cu2++e→Cu+
anode:2OH--2e→2H++O2↑
The entire process is not only a copper deposition reaction, but also an acid making process because oxygen runs away and H+、SO42- combine to form H2SO4.
Anti oxidation treatment
After being washed and dried, the copper foil peeled off from the cathode roll enters an acidic anti-oxidation solution containing H2CrO4. Under the action of direct current, a very thin and dense Cr3+salt anti-oxidation film is formed on the surface of the copper foil.
Structure diagram of new electrolysis machine:
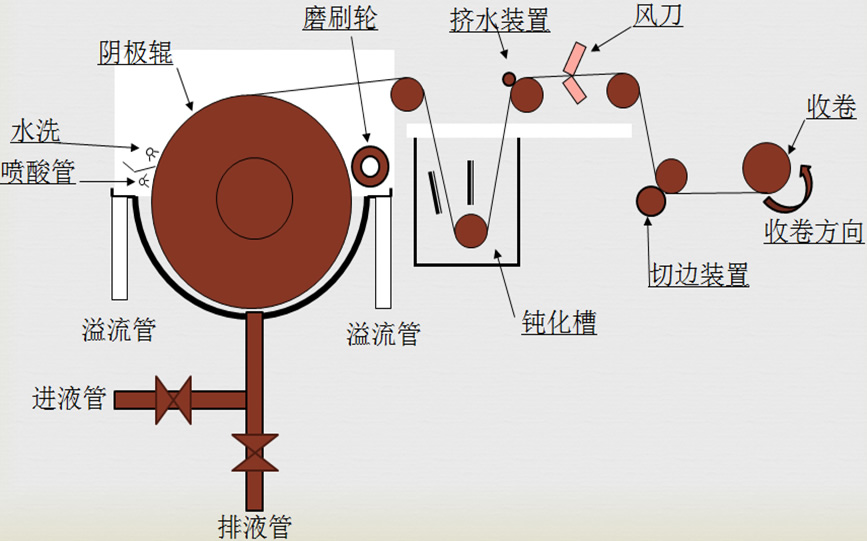
Structure diagram of electrolytic copper foil machine:
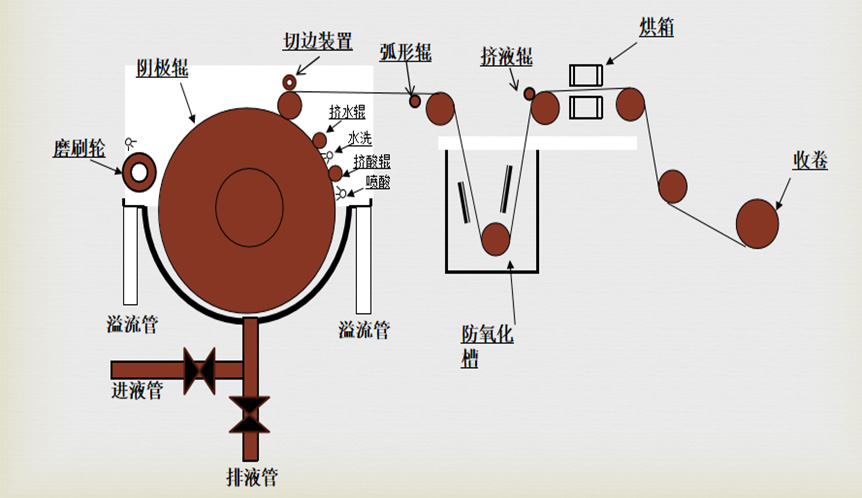
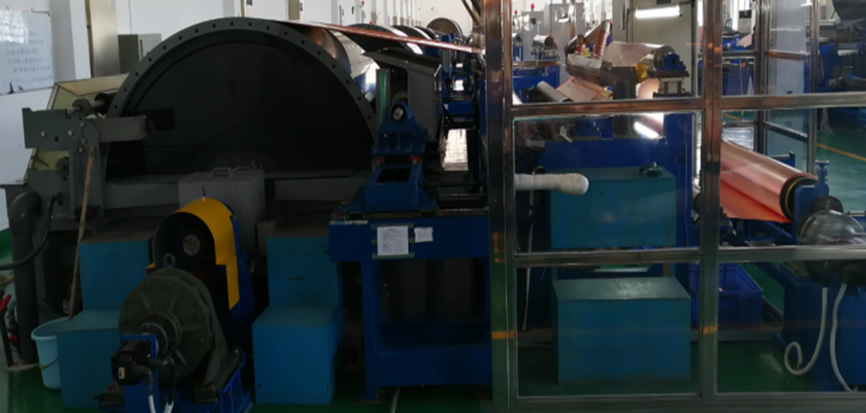
Physical picture of electrolysis machine:

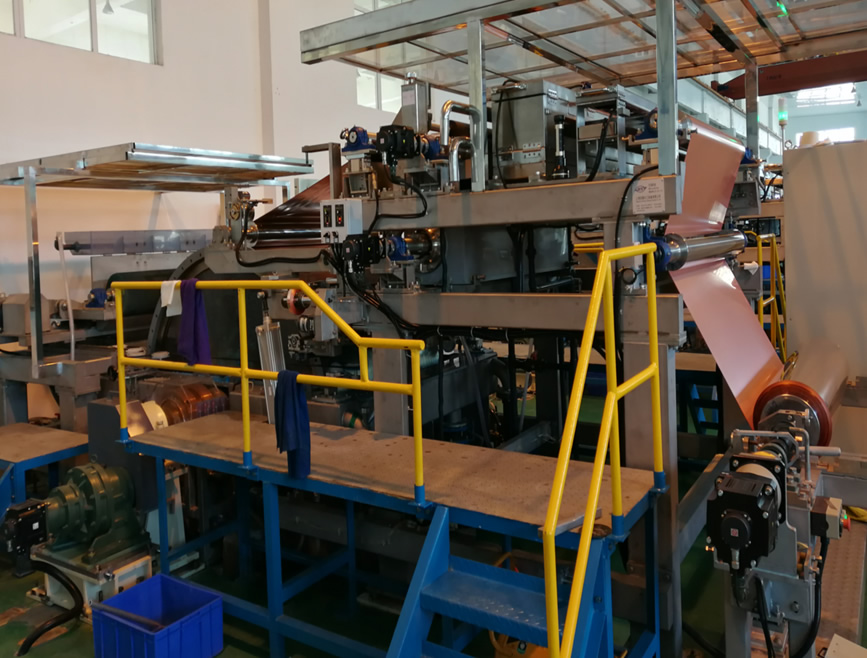
Physical picture of the new electrolytic machine:

3.Splitting & Packing

4、Product Technical Requirements
Industry execution standards:
• Electrolytic copper foil for lithium-ion batteriesDB44/T 837-2010
• Electrolytic copper foil for lithium-ion batteries SJ/T 11483-2014
1. Mass per unit:
• control standards
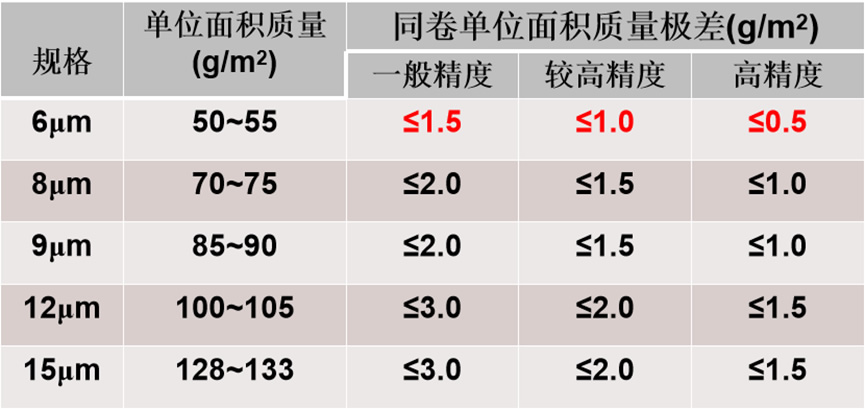
• Impact on customers
1) Resulting in inconsistent coating amounts of active substances between different rolls, affecting the consistency of the battery.
2) Under the same weight, the roll length decreases, increasing the production cost for customers.
3) Causing inconsistency in the size (thickness) of battery electrodes.
2. Tensile strength:≥294Mpa
Low - prone to wrinkling during production and customer use, prone to breakage of the polarizer, and prone to significant changes in polarizer size after coating with rollers.
3.Elongation rate:
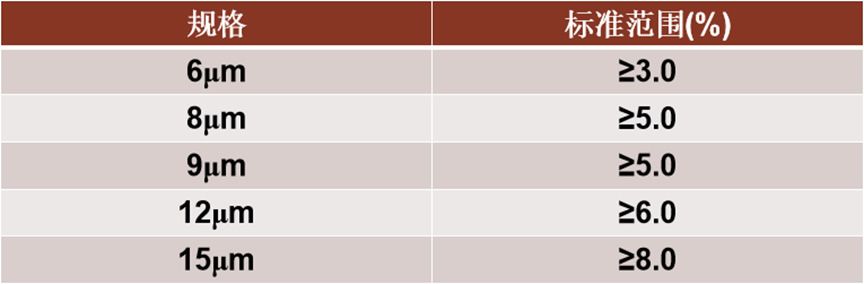
Low - prone to breakage during production and customer use.
4. Surface roughness:
Smooth surface Ra value: ≤ The arithmetic mean of the absolute distance between a point on the contour line along the measurement direction and the reference line within a measurement length of 0.30 μ m.
Surface Rz value: ≤ 3.0μm
The sum of the average of the 5 maximum contour peak heights and the average of the 5 maximum contour valley depths within the measured length.
Impact on customers: If both values are too high, it will result in a higher mechanical thickness of the copper foil.
5.Mechanical thickness:
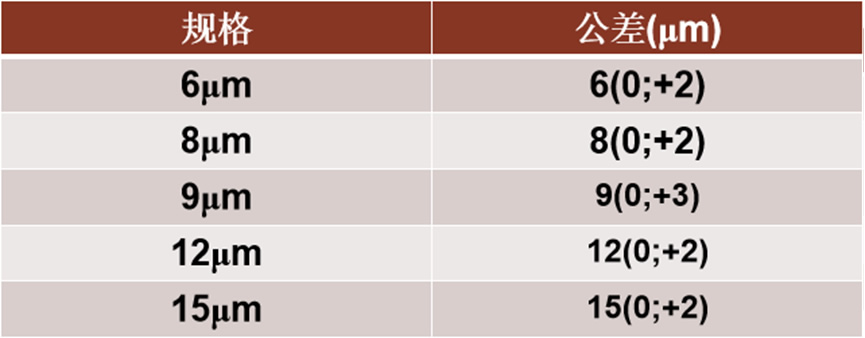
Impact on customers: causing excessive thickness of electrode plates, affecting battery assembly.
6. oxidation resistance:
Standard requirement: Bake at 140 ± 2 ℃ for 15 minutes without oxidation or discoloration.
General enterprise requirements: Bake at 150 ± 2 ℃ for 10 minutes without oxidation or discoloration.
Impact on customers: The oxidation resistance is not qualified, and the copper foil oxidizes when coated with negative electrode material, increasing the internal resistance of the battery.
7. appearance quality:
• Flat surface, uniform color, with oxidation discoloration, spots, wrinkles, indentations, and fingerprints; In any 300 × 300mm area of the sample, the number of non permanent indentations, continuous or periodic irregularities, and other defects shall not exceed one.
• Neat trimming, no gaps, tearing, curling, folding, or wavy edges; Allow electroplating stripes that do not affect the coating of negative electrode materials.
• Unless otherwise specified, the depth of scratches should be less than 5% of the nominal thickness, and the number of scratches in any 300 × 300mm area of the sample should be ≤ 1.
• The surface should be clean and free of dust, grease, salt, copper powder, stains, and other foreign objects that may affect processing and use.
8.Common appearance quality issues:
1) indentation
• Definition: The raised or depressed surface of a foil formed by the compression of solid particles (dust, copper powder, etc.), as shown in the following figure:

2) convex line
• Definition: The copper foil surface has a linear protrusion with a width of about 1-3mm, as shown in the following figure:

3)fold
• Definition: The copper foil surface has one or more raised diagonal stripes (forming an angle greater than or less than 90 ° with the length direction of the copper foil), with a width of about 2-5mm, as shown in the following figure:

4) White dot (white mark)
• Definition: Irregular white dots (prints) on the surface of copper foil, with varying sizes, as shown in the following figure:
5) Yellow dot (yellow seal)
• Definition: Irregular or regular yellow dots (marks) on the surface of copper foil, as shown in the following figure:

6) Fish scale pattern
• Definition: On the surface of a copper foil roll, there are fish scale wrinkles along the length direction of the copper foil, as shown in the following figure:

7) Horizontal wrinkles
• Definition: Form horizontal (perpendicular to the length direction of the copper foil) wavy soft folds on the surface of the copper foil, as shown in the following figure:

8)water ripple
• efinition: Form wavy stripes on the surface of copper foil, which are consistent with the length direction of the copper foil, as shown in the following figure:
